Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Applications in Food Safety–Review
Abstract
One of the primary goals and aims of studying chemistry in society is the promotion of the well-being of humanity and the sustainable utilization of the available resources. Chemistry has played a significant role in water treatment, food production, energy production, and medicine, among other critical areas of society. This study explored the utilization of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in the aspect of promoting food safety for human consumption. Various factors might affect the composition and storage of the food items in the society. Through the utilization of chemistry techniques such as (LC-MS), there can be Identification of the various aspects that require consideration in the Improvement of the different health and nutritional requirements that the food items are expected to have in society. As illustrated in this study, the analytical and technical aspects are highly influential in the determination of the proper measures for each component and the illustration of the various toxins that are likely to affect the overall food safety of the members of society in general.
Author Contributions
Academic Editor: Abu-Hussein Muhamad, Arab-American University
Checked for plagiarism: Yes
Review by: Single-blind
Copyright © 2024 Pradeep Sarkate
 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Citation:
Introduction
Food safety
Food safety is a cornerstone of public health, ensuring that food consumed by individuals is free from contamination and safe for consumption. It encompasses a comprehensive run of practices, policies and systems organized to keep foodborne illnesses precautionary to consumer health and raise general welfare. In modern society, food safety is of paramount importance due to the increasing complexity of food production methods and distribution systems. This Check delves into the implication of nutrient guard, the challenges it faces, and the measures that are inevitable to hold and better it in today's combined world, the grandness of nutrient safety 1. The primary role is protecting state health foodborne illnesses caused by pathogens such as arsenic salmonella escherichia coli, and listeria monocytogenes strike billions globally in each class. These illnesses can result in mild discomfort, severe complications or even death, specifically in vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly and those with weakened immune systems. Ensuring nutrient guards reduces the chance of such illnesses and joint health complications. There is also the aspect of the economic impact of foodborne diseases levy and significant efficient effect along with healthcare costs, productiveness losses, and costs associated with nutrient recalls and litigation 2. By preventing contamination, businesses and governments can save billions annually while maintaining consumer trust in the food supply chain.
When food is considered to be safe, there is an aspect of consumer confidence. A secure food supply fosters consumer confidence, which is essential for the role of local and global food markets. Scandals or outbreaks get fret bank up to cut use and efficient imbalance inside the nutrient industry. Another critical measure that can be employed in the food industry is sustainability and development. For example, it isn't easy to guard food for sustainable evolution 1. It ensures that food is not wasted due to contamination or spoilage and that supplies used in production, such as water, energy and labour, are not squandered.
There are challenges in ensuring food safety in society and also globally. They include the Globalization of food supply chains and the global nature of modern food production and trade, which increases the risk of contamination. Foods must go thousands of miles ahead and stretch consumers past the aggregate men and restrictive systems that get fancy traceability and enforcement of guard standards 2. There are also emerging pathogens and contaminants that change the husbandry mood of households, and layouts are conducted to address the problem of green foodborne pathogens and chemical pollutants. For example, antibiotic-resistant bacteria and mycotoxins present significant challenges 3. Through the concept of urbanization and changing lifestyles, there is the rise of fast food ready-to-eat meals, and dining out increases the complexity of maintaining food safety. Wrong treatment or store astatine whatever head inch the nutrient iron gets to run to contamination. There is also an inequitable approach to good food, especially for those who belong to different parts of society. In developing countries, short-base, modest approach to light sweat and mean restrictive frameworks aggravate nutrient guard risks. Meanwhile in developed nations, socioeconomic disparities can leave low-income populations more exposed to unsafe food 3. The concept of climate change has also affected food safety in the society. Rising temperatures and shifting weather Layouts influence food production and storage conditions, potentially increasing the prevalence of foodborne pathogens and spoilage.
There are strategies for ensuring food safety in society, such as the application of good agricultural and manufacturing practices. Focus on minimizing contamination during cultivation, harvesting and transportation of crops and livestock. The aim is to prevent contamination during food Methoding and packaging. Right, sanitization hygienics and gadfly checks are necessary PartsUtilization of hazard psychoanalysis and critical checkpoints (haccp) 4. Where it provides orderly access to distinctive and controlled nutrient-guard hazards and crucial points for the product and Methoding iron, it is widely adopted globally and ensures proactive risk management. There is also the incorporation of robust regulatory frameworks where governments must establish and enforce food safety regulations based on scientific evidence. Agencies are the America. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) play pivotal roles in setting standards and conducting inspections 4. There is also the need for food safety education and awareness; public awareness campaigns and teaching programs for food handlers are essential for fostering a culture of food safety. Educating consumers about the proper nutrient storage provision and hygienics creates significant cut risks. Advanced technologies also play a vital role through innovations such as arsenic blockchain for Problem iron traceability, fast characteristic Checks for pathogens, and prophetic Representation for chance judgement, which are revolutionizing nutrient guard. These technologies Improve transparency and enable quick Answers to potential outbreaks.
Global collaboration of organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) work with governments to harmonize food safety standards and coordinate Answers to global challenges. Initiatives care for the worldwide nutrient guard regime net (infosan) and help information joint during eCombinencies 5. There is also the role of individuals in nutrient safety and safe nutrient treatment practices. Individuals run amp relevant Role inch preventing pollution. Simple measures like washing hands using separate cutting boards for raw and cooked foods and cooking food to the appropriate temperatures can make a significant difference. There is also the aspect of proper storage of food items 5.Storing perishable items at the correct temperatures and adhering to expiration dates are complicated ways to prevent spoilage and bacterial growth. Increased advocacy for better standards can also be applied. Consumers can influence food safety policies and practices by advocating for stricter regulations, supporting ethical brands, and reporting safety violations.
Food Safety in the Digital Age can be illustrated through digital technologies that are reshaping food safety in several ways: Blockchain Tech enables end-to-end traceability, allowing stakeholders to track the journey of food products from farm to Branch. This foil helps important pollution sources quickly during outbreaks. Artificial word and car learning, through AI, get call nutrient guard risks away analyzing big Information sets such as arsenic endure Layouts Problem iron activities and accurate outbreak Information 6. There are also Smart packaging systems that get proctor nutrient character inch material sentence provision consumers with alerts if amp production is inadequate or compromised. There are e-commerce challenges that affect the food safety aspect, such as the rise of online nutrient pitches and market services necessitating tight Watching to check guard during store and transit.
The future outlook illustrates that as the round universe continues to arise, ensuring nutrient guard leave goes further necessary. Advances in Tech, stricter regulations and greater consumer awareness are likely to shape the future of food safety. Not-withstanding addressing inequities in the approach to good nutrients and mitigating the effect of mood shift leave rest critical challenges collaborative efforts between governments, industries, academia, and consumers leave work essential to make live nutrient systems that prioritize guard without vulnerable sustainability 6. By fostering innovation and emphasizing preventive measures, society can move closer to achieving universal access to safe and nutritious food. Food safety is a shared responsibility that underpins public health, economic stability and global development. In associate nursing, progressively, combined man maintaining nutrient guard requires alertness, Layout, and complete coaction of Astatine levels. Whether through Improved practices, technological advancements or education, prioritizing food safety ensures a healthier, more equitable society for present and future generations Figure 1.
Figure 1.Importance of food safety in society: https://restorapos.com/blog/why-food-safety-is-important
Role of chemistry in food safety
Food safety is a complicated public health concern worldwide, and it is essential to ensure that food is free from contaminants and safe for consumption. Chemical science plays a complex role in every aspect of the nutrient guard, from finding insidious substances to preserving nutrient character and enhancing nutrition. With advances in analytical methods, chemistry helps watch food production, method storage, and distribution, making it a cornerstone of modern food safety systems. Chemistry has a role to play in finding chemical contaminants. One of the principal roles of chemical science in nutrient guard is to identify and quantify contaminants in nutrients 7. These contaminants can be introduced during farming, such as storage or distribution, and can pose serious health risks. Some include pesticides and residues, which are comprehensive old-inch husbandry used to protect crops from pests. Their residues get rest along nutrient products. The chemical role is through advanced analytic techniques such as arsenic blow chromatography-mass spectroscopy (gc-ms) and precise chromatography-tandem lot spectroscopy (lc-ms/ms) are old to find and beat pesticide residues astatine line levels 8Another aspect deals with Heavy Metals, which are Toxic metals like lead cadmium arsenic. Mercury can contaminate food through soil, water or industrial Methods. Chemistry through Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS)enable precise finding of these metals, ensuring they remain within permissible limits. There are also mycotoxins and spurious toxins like arsenic aflatoxins that are produced away fungus kingdom inch grains insane and spices. Through chemistry, we are able to offer high-effectiveness precise chromatography (HPLC) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) to proctor and check these course-occurring toxins.
Food fraud and adulteration are challenges where food adulteration involves the addition of non-food substances or mislabeling to increase profits, compromising safety. The role of chemistry is to provide techniques like nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and Fourier-Revolutionize infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, which is used to confirm the authenticity and Find adulterants. There are also nutrient additives and preservatives. Chemistry is vital in the development of nutrient additives and preservatives that raise the spirit bet, give it a better texture, and hold nutrients. Antimicrobial agents can be used. Chemical preservatives such as benzoates, sorbates and nitrates inhibit microbial growth and spoilage. Their strength and guard are evaluated by hard chemic Checking Thee are also Antioxidants like ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and tocopherols (vitamin E), which prevent oxidative degradation in fats and oils, ensuring the stability of food products. Emulsifiers and stabilizers compound care lecithin and xanthan glue better the body and constancy of refined foods with their chemic interactions deliberate to Improve Effectiveness. Flavour Improver: Through chemicals such as monosodium glutamate (MSG) Improve taste. Toxicologic studies set their guard and admissible employment levels.
Chemistry can also assist in the concept of food preservation techniques. Food Preservation Technique Chemical principles underlie many preservation methods, ensuring food remnants are safe and consumable for extended periods. Infrigidation and freezing chemistry help read the molecular changes that occur during cold, such as arsenic frost quartz organization and enzyme action to denigrate character loss. Canning and Thermal Methoding, chemical reactions involved in heat treatment such as Maillard browning and protein denaturation, are Improved to kill pathogens while preserving nutrients. Limited air packaging (map) by fixing the frothy surround (e.g. Constructing c dioxide or n levels) chemical science prolongs ledge spirit and inhibits spoilage 9. The chemical method of fermentation is driven by microbial metabolism, which produces natural preservatives like lactic acid, which inhibit harmful bacteria. Nutritionary munition and improvement chemistry: Add up nutrients and guard away invigorating nutrients with essential nutrients to work deficiencies. Vitamin and Mineral Fortification can occur when chemistry ensures stability, bioavailability and homogeneity of added nutrients like iron in cereals or vitamin D in milk 9. Practical foods: chemical search supports the evolution of foods with extra health benefits such as arsenic probiotics or omega-3 fat acids enhancing general state health. Reducing Harmful Substances: efforts to reduce naturally occurring harmful compounds such as acrylamide in fried foods rely on chemical understanding of formation pathways and mitigation strategies. Restrictive frameworks and standards of chemistry play a vital role in establishing and enforcing nutrient guard regulations to protect consumers. Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs): Chemical analysis determines the MRLs for pesticides and contaminants, ensuring Compliance with international standards like those set by the Codex Alimentarius. Chance psychoanalysis and critical checkpoints (haccp) and chemistry help important points in nutrient products where pollution risks get work satisfied based on real-time analytic methods. Food Labeling chemistry ensures accurate labelling of nutritional content and allergens, empowering consumers to make informed choices.
Advancing technologies in nutrient safety advancements in chemical science are driving Layout inch nutrient guard addressing challenges posed by globalization and dynamic use Layout. Through the use of Nano Tech, nano sensors are being developed for real-time Detection of pathogens and contaminants, enhancing watching capabilities. There are also Biosensors that combine chemical science and biota biosensors to find particular toxins, allergens or pathogens with excellent 10. There is also the concept of Green Chemistry, where sustainable chemical methods are employed to reduce the use of synthetic additives and promote natural alternatives. Chemical science inch chance assessment risk judgement is an amp base of nutrient guards requiring amp sound because of chemic interactions and toxicology. Dose-Answer Relationships: Chemistry helps determine safe exposure levels for chemicals in food, balancing risks and benefits. Fundamental interaction studies, chemical interactions betwixt ingredients, packaging materials and environmental factors are deliberate in calling and palliating prospective risks. There are also Real-World uses like outbreak investigations 10, chemistry-acquired immune deficiency syndrome to trace the reference of pollution during foodborne malady outbreaks, exploitation methods care isotope ratio analysis, Allergen Checking, analytical chemistry Finds trace levels of allergens ensuring Compliance with food safety regulations for allergen labelling. Ensuring sustainability chemistry Adds to the development of safer pesticide reduction nutrient blow and promoting eco-friendly packaging materials
There are various challenges and future directions in which chemistry is likely to take to assist in solving the issues concerning food safety in society. Such matters include Globalization, the global nutrient problem, and iron increases the complexity of nutrient guard watching. Chemistry provides tools to address this by standardizing Checking methods globally 11. Environmental changes Environmental changes affect nutrient guards such as arsenic hyperbolic mycotoxin products in crops. Chemical research is essential to developing mitigation strategies. Consumer awareness chemistry plays a Role in educating consumers about the nutrient guard and the skill seat additives, preservatives and contaminants. Chemistry is intrinsic to ensuring that the nutrient guard is associated with nursing and progressively compounds around the nutrient unit. From Finding contaminants and developing preservatives to enhancing nutrition and enforcing regulations, chemical science underpins every aspect of food safety 11. Recent technologies and sustainable practices keep up with the role of chemical science, addressing contemporary challenges and ensuring the health and welfare of consumers. As food safety becomes more complex, the intersection of chemistry and food science will remain pivotal in safeguarding public health.
Determine food safety through the use of chemistry
Ensuring food safety is decisive in protecting public health and preventing contamination-related illnesses. Chemical science plays a vital role in finding distinctive and quantifying insidious substances and inch nutrients. Various analytical techniques are used to examine food samples for contaminants such as pesticides, toxins, heavy metal pollutants, and microorganisms. This Check delves into the lead methods engaged in nutrient guard psychoanalysis in chemical science, including spectrometry chromatography lot spectroscopy, immunoassays and molecular techniques.
Chromatographic Techniques: Chromatography is one of the most widely used techniques for food safety analysis due to its ability to separate Complicated mixtures. The principal types include Liquid Chromatography (LC), which separates analytes in a liquid mobile phase based on their interactions with a stationary phase and is commonly coupled with analyzers like UV-Vis spectrometry or mass spectrometry (LC-MS) 12. It is applied in pesticide residues, finding organophosphates, carbamates and neonicotinoids in fruits and vegetables. Mycotoxins allow Identification of aflatoxins and ochratoxins in grains and nuts. Gas chromatography (GC) utilizes a frothy versatile stage to break fickle compounds, often one with a lot of spectroscopy (gc-ms) for increased sensitivity 12. It is applied to find fickle natural compounds (VOCs) and impurities, care for benzene, and watch pesticide residues in oil-based or refined foods. Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) allows the separation of compounds based on their molecular size. It is applied in the analysis of polymer additives in food packaging. They are determining the protein content in foods.
Spectroscopical techniques and spectroscopy involve the fundamental interaction of electromagnetic radiation with problem provision, as well as other qualitative and decimal information. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy: Measures the absorption of UV or visible light by analytes. It is used to quantify food additives like dyes and preservatives and find contaminants such as melamine in dairy products. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy explores molecular vibes to important practical groups 13. It is applied to find pabulum anoint adulteration and confirm nutrient legitimacy, e.g., decisive honey lines. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) and Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES): Examine trace levels of heavy metals like lead cadmium and arsenic. It is used to Watch for heavy metal contamination in seafood and drinking water and Ensure Compliance with regulatory limits. Nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) spectroscopy: provides Fancy Roleal Information about molecules 13. It is utilized to identify nutrient hoaxes such as arsenic mislabeling or debasement of high-value products, coloured oil, and watching ferment. Methods
Mass Spectrometry (MS): Mass spectrometry identifies compounds by analyzing their mass-to-charge (m/z) ratios. Much one with chromatography (e.g. lc-ms or gc-ms) manuscript Improves the sensibility and specificity of nutrient guard analysis it is used contaminant finding 14: identifies buck contaminants such as arsenic vet dose residues in meat, food validation it differentiates betwixt good and base nutrient products and toxicology studies identifies mycotoxins spurious toxins and counterfeit contaminants.
Immunochemical Methods: Immunoassays utilize the specificity of antigen-antibody interactions to Find specific compounds. It can be illustrated as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent Check (Elisa) and a highly tender facility for Finding proteins, toxins, and allergens. It is used in watching allergens care, gluten peanuts and milky proteins and finding aflatoxins and different mycotoxins 14. In the case of Lateral Flow Assay, it is rapid and operator-friendly and often used for field checking. It is applied to find antibiotic residues in milk and Screen for pathogens like Salmonella and E.coli in green foods. It is utilized in high sensibility and selectivity while being fast and cost-effective compared to chromatographical techniques.
Molecular techniques and advances in molecular biology have introduced DNA and RNA-based methods to find microorganisms and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in food. Polymerase chain reaction(PCR) amplifies particular deoxyribonucleic acid sequences for distinctive pathogens or GMOs. It is used in finding bacterium care listeria salmonella and campylobacter and confirming the bearing of GMO ingredients 14. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS):, which provides comprehensive genomic analysis of microbial communities. It is applied to watch microbiota in fermented foods. They also trace contamination sources in outbreak investigations. Electrochemical methods: electrochemical sensors beat changes in electric properties, causing the bearing of particular analytes to be away. It is applied in Finding foodborne pathogens via biosensors and watching gall indicators care ammonium hydroxide or fickle amines inch fish.
The physical and thermal analysis includes derivative scanning calorimetry (DSC) to measure warmth run-inch reaction to temperature changes. It is applied to assess the constancy of nutrient emulsions characterizing fats and oils. Rheology evaluates the mechanical properties of food materials. Ensure consistent texture and quality in Methoded find fraudulent additions such as thickeners in beverages 14. Fast examination kits are applied in commercial kits to render point-of-care examinations for prompt decision-making regarding nutrient safety. They include check strips for pesticides in vegetables and colourimetric assays for them. They are applied to find spoiled inch dairy farm products and challenge nutrient guard analysis. Despite their Effectiveness, these methods look at respective challenges:
There are various challenges encountered in the chemical analysis of food. Complicated matrices: foods bear different compositions, making it challenging to sequester analytes without interference. Cost and accessibility: Advanced techniques care lc-ms and ngs take important investing and expertise. Standardization: variance inch methods get run to incongruous results over laboratories. Emerging contaminants: the rise of green pollutants such as arsenic microplastics necessitates wise development
Specific trends will impact the utilization of chemistry from the perspective of food analysis. They include advancements in analytic chemical science, such as drive layout inch nutrient guard analysis and the use of portable devices and handheld spectrometers and sensors for on-site checking. Green chemistry incorporates eco-friendly reagents and energy-efficient instrumentation. The utilization of ai-powered tools for information psychoanalysis anomalousness espial and wise optimization, and the integration of techniques: union aggregate methods such as arsenic lc-ms with iridium spectrometry for general analysis food guard psychoanalysis relies on along amp different armoury of chemic methods apiece bespoke to find particular contaminants and check deference with restrictive standards. Techniques such as chromatography, spectroscopy immunoassays, and molecular biology have revolutionized food safety, offering unparalleled sensitivity and specificity. Arsenic challenges care compound matrices and nascent contaminants run the current Layout, and the consolidation of advanced technologies fosters the increase in the dependability and productivity of nutrient guard assessments.
Mass spectrometry
The Figure 2 below illustrates the mass spectrometry diagram: -
Figure 2.Mass spectrometry diagram from https://byjus.com/chemistry/mass-spectrometry/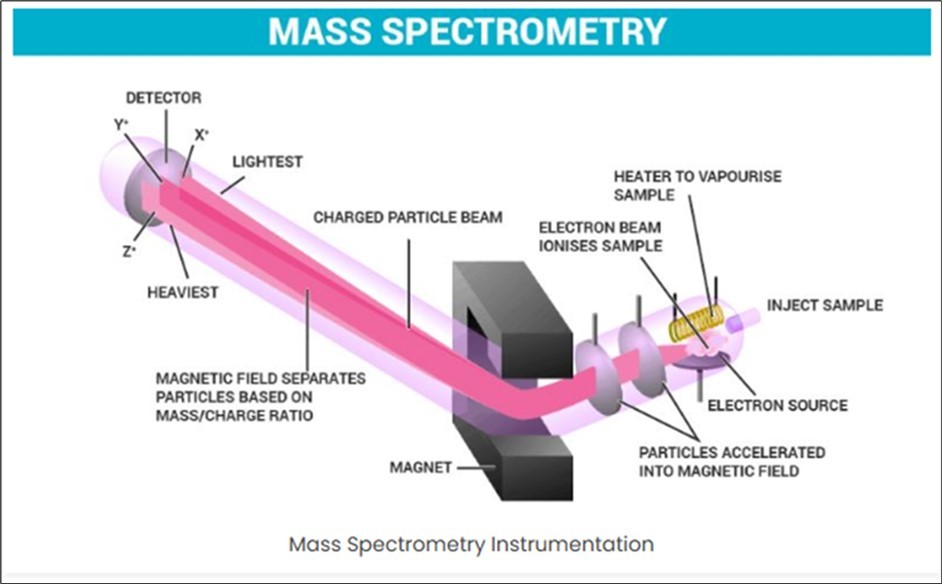
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of ions. It is the right drive for distinctive and quantifying chemic compounds and analyzing molecular structures. The fundamental structure of a mass spectrometer involves several important Parts, each with a specific Role to achieve the separation analysis of ions 15 the significant Parts are arsenic as follows: the first part is the sample introduction system. The purpose of this aspect is to introduce the sample into the ionization chamber in a controlled manner without compromising the vacuum of the mass spectrometer. Various methods are applied, including direct insertion, where the sample is introduced directly via a probe. Gas Chromatography (GC-MS) separates volatile compounds before entering the MS 15. There is also liquid chromatography (LC-MS), which has candles with non-volatile or thermally labile compounds. There is also the ionization source, which converts the taste molecules into ions arsenic, the lot mass spectrometer, and Examines live particles. Different types of ionization can be applied, including electron ionization (EI), which bombards molecules with high-energy electrons up to fragmentation., 15. There is chemical ionization (ci), which uses ion-molecule reactions to get ions, many concessions inferior fragmentation. It can also be carried out through electrospray ionization (esi): green for biomolecules; Produces ions from amp unmistakable taste exploitation amp dynamic field; and finally, there is matrix-assisted optical maser desorption/ionization (MALDI): abstract for significant biomolecules care proteins; uses amp optical maser and amp intercellular substance to ionize the sample.
The third aspect deals with the mass analyzer that separates ions based on their m/zratios using electromagnetic fields. Such analysis can be carried out through Quadrupole, which uses oscillating electric fields to filter ions of specific m/z values. There is also the Time-of-Flight (TOF), which measures the time it takes for ions to travel a set distance; lighter ions arrive faster 16. Further, there is the magnetic Sector, which uses a magnetic field to bend the trajectory of ions. Separation depends on their The Ion Trap method can be applied, which traps ions in a three-dimensional electric field and ejects them sequentially for analysis. There is also Fourier Revolutionized Ion Cyclotron Resonance (FT-ICR), which provides high resolution and Precision by analyzing ion motion in a magnetic field.
Mass spectrometry also has detectors that convert the apart ions into a vital point, typically electrical. There are different types of detectors, including electron multiplier, which amplifies the point produced when ions hit their surface. 16. There is the Faraday cup, which measures the flow produced away ions directly inferior to tender but robust. Finally, there is the microchannel home detector that offers great sensibility and prompt reaction times. The last aspect is the information method system that examines and Imagines the output producing a mass spectrum, which is a plot of ion intensity versus m/z. The primary importance of mass spectrometry is that it Identifies molecular weights, structural fragments and isotopic Layouts and also Quantifies the relative abundance of Parts in a sample.
Comparison Between Tandem Mass Spectrometry and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) has become an essential analytical technique for studying the structure composition and quantity of molecules across diverse fields. ii advance approaches inch ms—tandem lot spectroscopy (ms/ms) and high-resolution lot spectroscopy (HRMS)—serve reciprocal roles apiece excelling inch particular sues 17. While MS/MS is widely used for structural elucidation and targeted analysis, HRMS provides unparalleled Precision in determining molecular masses and Finding Complicated mixtures. This Check explores the principles, advantages, limitations and Uses of ms/ms and HRMS, highlighting their name differences and synergies
Tandem mass spectrometry principles (ms/ms) involve ii or further stages of lot psychoanalysis. The main principle is to isolate a precursor ion fragment into smaller ions (product ions) and Examine these fragments to gain structural understanding 18. The Ion Selection (MS1) is needed to illustrate this concept: It highlights that a specific ion of interest known as the precursor ion is selected based on its mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) in the first mass analyzer. There is also the aspect of fragmentation, which illustrates that the selected precursor ion undergoes controlled fragmentation typically via collision-induced dissociation (CID), electron-capture dissociation (ECD) or higher-energy collisional dissociation (HCD) in a collision cell 18. There is also the Product Ion Analysis (MS2): The resulting fragment ions are Examined in the second mass Examiner, producing a spectrum that provides structural information.
Principles of High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS)
The following are some of the principles in high-resolution mass spectrometry, which is characterized by its ability to measure ions' m/z with extremely high Precision and resolving power. This preciseness allows for characteristic betwixt ions with about congruent mass, making it difficult for the HRMS to be used for compound mix analysis. The resolving power and high accuracy δm is the minor mass difference between two different peaks. HRMS instruments achieve resolution exceeding 100000 17. There is also the accurate mass measurement: HRMS provides molecular formula determination by calculating exact masses to several decimal places, distinguishing between molecules with similar nominal masses. The instrument types that are applied include Fourier Revolutionize Ion Cyclotron Resonance (FT-ICR) and Orbitrap Examiners, which are common HRMS systems that offer exceptional resolution and mass precision.
Differences Between MS/MS and HRMS
| Characteristic | Tandem Mass spectroscopy | High-resolution mass spectrometry |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Structural elucidation and targeted analysis of molecules | Accurate mass measurement and analysis of complicated mixtures |
| Ion selection | Focuses on precursor and product ions for structural details | Examines all ions simultaneously without fragmentation |
| Resolving power | 1000 to 10000 | Above 100,000 |
| Precision | It relies on m/z isolation and controlled fragmentation | Determines exact molecular formulas with sub-ppm precision |
| Fragmentation | Archived through CID, ECD OR HCD | Fragmentation is optional |
| Quantification | Highly sensitive to targeted compounds | Less sensitive for targeted quantification or excels in untargeted analysis |
| Uses | Highly utilized in metabolomics and drug analysis | Unknown compound identification |
In tandem, mass spectrometry obtains structural information from fragmentation. Layouts provide detailed structural Understandings, including Roleal groups and bond arrangements. There is also the application of Targeted Analysis where techniques like Selected Reaction Watching (SRM) and Multiple Reaction Watching (MRM) enable precise quantification of specific molecules in Complicated matrices. The process is Susceptible, making it ideal for low-abundance analytes. The process is versatile as it is suitable for a wide range of molecules, from small metabolites to large biomolecules like peptides and proteins. The limitations of this process include the fact that it has a limited scope18. They are primarily suited for targeted studies and not as practical for untargeted analyses. There is complicated instrumentation that requires precise synchronization. The doctors require ionization before the separation of the fragmentation. Uses of Tandem Mass Spectrometry include Identifying and sequencing peptides and proteins through fragmentation, analyzing metabolic pathways, identifying specific metabolites and finding and quantifying drugs and their metabolites in biological samples—screening for genetic disorders or biomarkers for diseases Table 1.
On the other hand, in high-resolution mass spectrometry, there is high resolving power that can distinguish between isobaric species (compounds with the same nominal mass). Accurate Mass Measurement that determines molecular formulas aiding in the Identification of unknown compounds. Broad 18. Applicability is ideal for untargeted analysis, enabling the study of Complicated biological samples without prior knowledge of the analytes. Isotopic resolution can also be identified where layouts provide an Understanding of molecular composition. There are several limitations that can be illustrated through this method. They include the cost of purchase, high purchase, and maintenance costs that limit its accessibility. There is also information where extensive information sets are produced that require sophisticated software and expertise to explain. There is Lower Sensitivity for Targeted Analysis. While excellent for untargeted studies, HRMS may not match the sensitivity of MS/MS in Finding specific low-abundance analytes 17. Uses of High-resolution Mass Spectrometry include Resolving and identifying Parts in mixtures like crude oils or environmental samples, Finding novel biomarkers in biological fluids for disease diagnosis, identifying trace amounts of unknown compounds in criminal investigations and determining the structures of Complicated natural compounds.
The combination of tandem mass spectrometry with HRMS (HRMS/MS) Combines the strengths of both approaches. This crossbreed facility provides fancy role information with great truth facultative advanced uses like identifying obscure metabolites and collateral structures done by atomization layouts. High-resolution atomization information acquired immune deficiency syndrome inch peptide sequencing and post-translational change studies Resolves isobaric variety spell provision Roleal information 18. The future direction of the mass spectrometry methods includes miniaturization and accessibility: Advances in instrumentality have cut the size of ms/ms and HRMS systems, widening their accessibility. They are using artificial word (ai) inch information analysis. AI acquisition procedures exist and are mature enough to work on the complexity of hrms and ms/ms. Information sets up psychoanalysis race and Precision. Coupling ms/ms and HRMS with techniques such as care blow or precise chromatography (gc-ms lc-ms) Improves the interval and espial of compound samples.
Tandem lot spectrometry (ms/ms) and high-resolution r lot spectroscopy (HRMS) are both problematic tools in contemporary analytic skills. MS/MS excels in targeted analysis and structural elucidation through fragmentation, while HRMS provides precise mass measurements and untargeted analysis capabilities 17. Their reciprocal strengths make them suitable for a comprehensive range of uses, from proteomics and dose evolution to environmental watching and biomarker finding. As Tech advances, the integration of these techniques will continue to expand their utility, providing a deeper understanding of the molecular world.
Liquid Chromatorgraphy
Liquid chromatography (LC) is a widely used analytical technique for separating, identifying and quantifying Parts in a fluid mixture. It relies on the derivative fundamental interaction of compounds with amp fixed stage and amp versatile stage facultative suitable interval founded along natural and chemic properties care sign sized and charges .liquid chromatography plays amp rugged Role inch different fields including pharmaceuticals nutrient guard environmental and biochemistry, 19. This document provides an overview of the principles, types, Uses, advantages and limitations of LC.
Principles of Liquid Chromatography
The basic principle of LC involves the distribution of solutes between two phases:
A. Stationary Phase: A solid or liquid material that Remnant fixed in the column.
B. Mobile Phase: A liquid solvent that flows through the stationary phase carrying the sample Parts.
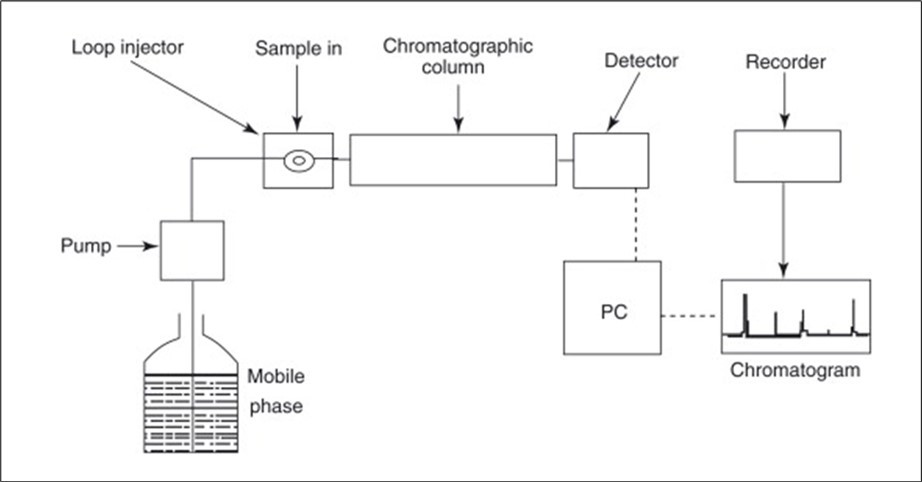
When a liquid sample is introduced into the system, its Parts interact differently with the stationary and mobile phases based on their chemical and physical properties. These interactions set the race astatine which apiece factor travels done the unit consequent inch their separation important Parts of associate in nursing lc system; solvent reservoir: contains the versatile stage which gets work amp one thinner or amp mix of solvents. A pump delivers the versatile stage of astatine amp coherent run order and pressure19. The injector introduces the taste into the versatile stage either manually or automatically—column: The effect of the lc unit compacting with the fixed stage. Columns vary in material size and Roleality depending on the Use. The analyzer finds separated Parts as they elute from the column, producing a signal proportional to the concentration of each Part. Green admits uv-vis fluorescence and lot spectrometry Information system: collects Methodes and displays information arsenic amp chromatogram display peaks like to person parts Figure 3.
Types of Liquid Chromatography
High-performance chromatography (HPLC): a highly sophisticated cast of LC that operates low force for quicker and further prompt separations. It is used in pharmaceutic psychoanalysis character checks and biomolecular studies 19. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography (plc) is an advanced Explanation of HPLC that uses small atom sizes and higher pressures for excellent resolution and speed. Used in fast psychoanalysis and high-resolution separations Normal-phase chromatography (NPC) can be utilized cold fixed stage and amp non-polar versatile phase Used interval of non-polar compounds and lipids Reversed-phase chromatography (RPC): the about green facility exploitation amp non-polar fixed stage and amp cold versatile phase, 20. Used in psychoanalysis of peptides proteins and mean natural molecules Ion exchange chromatography allows to separates molecules founded along their point exploitation amp live fixed phase Used in psychoanalysis of aminic acids proteins and nucleotides Size-exclusion chromatography that separates molecules founded along sized away exploitation amp permeable fixed phase; it applies for molecular angle and polymer analysis, 20. Affinity chromatography. Relies on particular interactions betwixt the fixed stage and the point particle (e.g. antigen-antibody binding), Used in the purification of biomolecules care enzymes and antibodies
Uses of liquid chromatography
In the pharmaceutical industry, to quality check and honour psychoanalysis of drugs identification of dynamic pharmaceutic ingredients (APIs) and abasement products. It can be applied to food safety. The findings of contaminants such as arsenic pesticides, mycotoxins, and adulterants, as well as the analysis of nutrient additives and nutritionary components, are essential 20. It is applied in environmental analysis to find pollutants such as arsenic pesticides, herbicides, sound metals, inch sweat, and ground samples. Applied in biochemical research: purification and psychoanalysis of biomolecules such as arsenic proteins nucleotides and carbohydrates separation of compound natural mixtures. It is utilized in forensic science analysis of drugs, toxins and different substances in natural samples for wrong investigations.
Advantages of liquid chromatography
It has versatility and is hence applicable to a comprehensive range of compounds, from mean natural molecules to significant biomolecules. It has a higher resolution and thus provides a superior interval of compound mixtures. It can be applied for both quantitative and qualitative analysis and, therefore, offers both recognition and correct quantification of analytes 20. Its mechanization, like modern LC systems, enables high-throughput psychoanalysis with nominal hand-operated intervention. It can be merged with other analyzers and hence can work organically with lot spectroscopy (lc-ms) for Fancy Roleal analysis.
Limitations of clear chromatography
The cost aspect is a limiting factor. The method requires costly equipment and maintenance. The sample preparation is accomplished by natural or environmental samples, which are comprehensively prepared. The solvent usage of large amounts of natural solvents is necessary to lift environmental and guard concerns. It is time-consuming, while Uplc speeds up the process of leading psychoanalysis around lc techniques, notwithstanding the importance of taking essential sentences for compound separations. The column lifespan is low; columns get demeaned across sentences, specifically with extremely compound or dirty samples.
There are various trends in green chromatography development, such as the development of eco-friendly solvents and solvent-free techniques to denigrate environmental impact. Miniaturization is where portable and micro-scale LC systems are used for on-site and point-of-care uses. Improved sensitivity; thus, there is integration with advanced unique systems care high-resolution lot spectroscopy (HRMS). Artificial intelligence is used to optimize interval conditions and analyze chromatographical information. Liquid chromatography is a base of contemporary analytic skills that offer unique versatility and preciseness for separating and analyzing compound mixtures. By leveraging advancements in instrumentation and finding methods, LC continues to play a vital role in diverse fields, ensuring the quality, safety and efficacy of products while advancing scientific research. Arsenic, the facility develops its effect in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to environmental skills, which is a lot to arise and foster.
Determination of food safety using LC-MS
The safety of food products is a problematic concern globally due to its impact on public health trade and regulatory Compliance. Nutrient pollution from pesticides, vet drugs, spurious toxins, and pollutants poses significant risks to man's health. Analytical techniques are essential for watching and enforcing safety standards. Among these, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) has been combined as a powerful tool due to its sensitivity, specificity, and versatility.
Principles of LC-MS
LC-MS combines two robust analytical techniques: liquid chromatography (LC) and mass spectrometry (MS).Liquid Chromatography: Separates Complicated mixtures based on physicochemical properties such as polarity size or ionic interactions. It employs a precise, versatile stage to bear the taste done at the fixed stage, typically amp tower compact with particular materials mass spectrometry 21: identifies and quantifies compounds found along their mass-to-charge (m/z) ratios. After separation by LC, analytes are ionized in the MS system; their ions are Found and examined to determine molecular weights and structures.
The synergy of LC and MS enables:
I. Selective Separation: LC ensures effective separation of compounds in Complicated food matrices.
II. High Sensitivity and Specificity: MS allows the finding and Identification of analytes at trace levels with minimal interference.
LC-MS Workflow in Food Safety Analysis Figure 4
Figure 4.LC-MS workflow: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361414266_A_fast_and_sensitive_absolute_quantification_assay_for_the_detection_of_SARS-CoV-2_peptides_using_parallel_reaction_monitoring_mass_spectrometry/figures?lo=1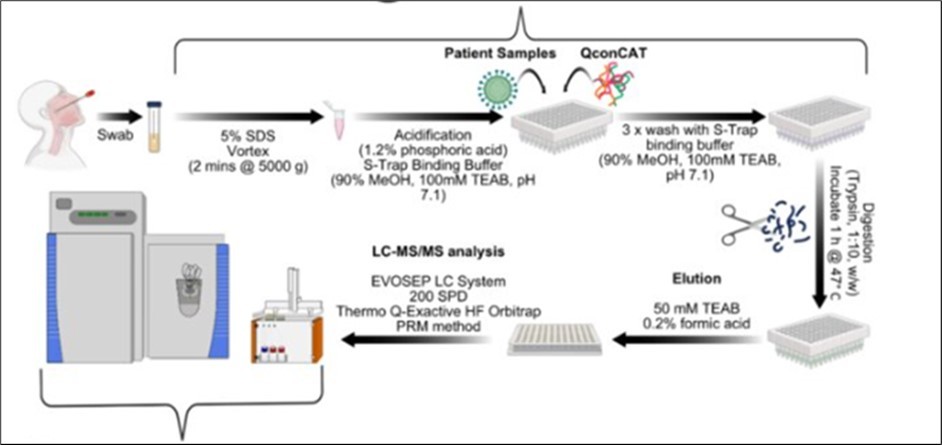
Sample Preparation
· Remove: Methods like QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective Rugged and Safe) are commonly used to remove contaminants from food matrices.
· Cleanup: Techniques like solid-phase Removeion (SPE) or dispersive SPE remove matrix interferences.
· Concentration: Samples are often concentrated to Improve sensitivity.
Liquid Chromatography: Select an appropriate column and mobile phase (e.g. water and acetonitrile). Adjusts conditions such as gradient elution to separate compounds effectively.
Mass Spectrometry and ionization Techniques: Electrospray ionization (ESI) and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) are commonly used. Modes: Single-stage MS (MS) or tandem MS (MS/MS) Improves specificity for Complicated matrices 21 (. Information Analysis: sophisticated software matches Finded ions against libraries for compound identification.
Uses of LC-MS in Food Safety
Pesticide residues are incredibly extensively used in old-inch husbandry to protect crops; only residues and nutrients get set health risks. LC-MS is the gold standard for pesticide analysis due to Its ability to Find multiple pesticide residues in a single run (multi-residue analysis). Sensitivity to parts per billion (ppb) or lower. Examples: Watching organophosphates, neonicotinoids and carbamates in fruits and vegetables. Complying with maximum residue limits (MRLs) set by regulatory bodies like the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. Environmental Security Way (EPA) Veterinary Drug Residues, Veterinary drugs such as antibiotics and growth promoters used in animal husbandry can leave residues in meat milk and eggs. Rest drugs care tetracyclines sulfonamides and β-agonists are Watched exploitation lc-ms. Ensures deference with secession periods. Prevents wonder drug opposition. Watching outlaw wonder drug use.
Mycotoxins are toxic secondary metabolites produced by fungi contaminating grains, nuts and dairy products. Green mycotoxins admit aflatoxins, ochratoxins and fumonisins. It provides excellent specificity for Finding and quantifying aggregate mycotoxins simultaneously. Ensures nutrient meets guard standards such as arsenic, which lot away the codex alimentarius Adulterants and Food Fraud 22; mis labeling compromises food safety and consumer trust. Examples include cyanuramide inch milky soudan dyes, inch spices, and black additives, identifying obscure adulterants away, generating Roleal information, finding efficient debasement such as arsenic, and replacing high-value ingredients with cheaper alternatives. Natural toxins such as cyanogenic glycosides, algal toxins and plant alkaloids can contaminate food and water sources.LC-MS Finds domoic acid and saxitoxins in seafood to prevent neurotoxic effects from harmful algal blooms.
Nutrient allergens: undeclared allergens such as arsenic, little proteins, or gluten set risks to individuals with allergies. Identifies allergenic proteins and peptides with great Precision. It approves nutrient labelling to check consumer safety packaging Contaminants 22; Food packaging materials can leach harmful chemicals like phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA) into food.LC-MS identifies and quantifies leachables to ensure Compliance with food-contact material regulations.
Advantages of LC-MS in Food Safety
High Sensitivity and Selectivity, thus, find contaminants at trace levels with minimal false positives. Versatility, hence, is able to examine a broad spectrum of compounds in diverse food matrices. They are applied in both Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis to quantify and identify contaminants simultaneously 22. Assist in the multi-residue analysis, hence examining multiple pollutants in a single run, saving time and supplies. It is used for regulatory Compliance and thus meets stringent requirements set by organizations like Codex Alimentarius FDA and EFSA.
Challenges in LC-MS-Based Food Safety Analysis
In complicated food matrices, Differences in protein lipids and carbohydrates can complicate the analysis. Requires extensive sample preparation. High operational costs, such as equipment maintenance and consumables, are expensive. Demands skilled operators for optimization and troubleshooting. Standardisation Problems: there is variability in methods that can hinder reproducibility across laboratories. Stad standardized Ruless are decisive for global trade. Emerging Contaminants: Novel compounds such as microplastics and nanoparticles require tailored LC-MS methods.
There are advancements in LC-MS for food safety, such as high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS). Instruments like time-of-flight (TOF) and orbitrap MS provide accurate mass measurements, improving compound identification. Miniaturization, such as Micro-LC-MS systems, reduces solvent usage and analysis time while maintaining sensitivity. Mechanisation and Robotics, like automating sample preparation, Improve throughput and consistency 23. Real-time watching, like Inline LC-MS systems, enables continuous Watching during food production. Green Analytical Chemistry, like Eco-friendly solvents and energy-efficient systems, align with sustainability goals. Calculator learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for AI-driven software assists in Information explanation method development and Oddity finding.
Real-World Uses
Pesticide rest psychoanalysis inch fruits, an lc-ms/ms read Examined 250 pesticide residues inch citrous fruits achieving espial limits under restrictive thresholds. The method demonstrated rapid analysis and Compliance with EU standards. Mycotoxin testing, lc-ms, was used to check for aflatoxins in corn samples from developing countries 23. The results informed mitigation strategies for reducing health risks. Extraneous espial in dairy farm products, a read old lc-ms to find cyanuramide inch baby rule revelation pollution astatine levels insidious to infants. The findings prompted stricter regulatory measures.
Regulatory Frameworks for Food Safety include Codex Alimentarius, which provides international food standards and guidelines for contaminants, and LC-MS methods that align with Codex requirements for MRLs and tolerances.; European Union (EU): Enforces strict pesticide regulations through Regulation (EC) No 396/2005. Fosters LC-MS for routine Watching. In the United States: The FDA and USDA use LC-MS to watch veterinary drug allergens and other contaminants' Compliance with tolerances listed in the CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) 23. LC-MS has revolutionized food safety analysis by offering unparalleled sensitivity, specificity and versatility. It has a good base for watching contaminants, ensuring restrictive deference, and protecting state health. As Tech advances, LC-MS systems are expected to become more accessible, Simplified and environmentally sustainable, further enhancing their role in safeguarding the global food supply.
Studies that have applied the use of LC-MS in food safety analysis
A study by Bessaire et al 2019 to evaluate the performance characteristics of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry procedure for the simultaneous determination of 12 mycotoxins in food, which were ochratoxin A, aflatoxins B1,B2,G1,G2, and M1, deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, fumonisins B1 and B2, and T-2 and HT-2 toxins. The method combined the simplicity of the QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Efficient, Rugged and Safe) approach with the efficiency of immunoaffinity column cleanup. The study Illustrated that it was applicable regardless of the food, the regulated mycotoxin, and the concentration level, and thus is an excellent candidate for future standardization. Other researchers, such as Jozinović et al., 2019 developed a liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of acrylamide and hydroxy methyl furfural (HMF) in corn snack products enriched with food industry by-products: brewer's spent grain (BSG), sugar beet pulp (SBP) and apple pomace (AP). Arce-López et al. (2020) Used high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (triple Quadrupole). The studied mycotoxins were: de epoxy-deoxynivalenol, aflatoxins (B1, B2, G1, G2 and M1), T-2 and HT-2, ochratoxins A and B, zearalenone, sterigmatocystin, nivalenol, deoxynivalenol, 3-acetyl deoxynivalenol, 15-acetyl deoxynivalenol, neosolaniol, diacetoxyscirpenol and fusarenon-X. The recovery was obtained in intermediate precision conditions and at three concentration levels. De Santis et al., 2017; wide range of matrices susceptible to mycotoxin contamination and the possible co-occurrence, a multi-mycotoxin and multi-matrix method was validated in liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) with the purpose to overcome specific matrix effects and analyze complex cereal-based samples. Bae et al., 2023; investigated pesticide residue levels in 535 domestically distributed agricultural products in South Korea using multi-residue analysis. Agricultural products from 13 regions, including Seoul, were pretreated using QuEChERS and d-SPE and subsequently analyzed using LC-MS/MS. They were able to identify the most frequently detected pesticides were dinotefuran (91), carbendazim (75), tebuconazole (61), and pyraclostrobin (59)Braun et al., 2018.; development and application of a highly sensitive, specific, and quantitative assay assessing up to 28 mycotoxins, including regulated (aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, deoxynivalenol, zearalenone) and emerging mycotoxins as well as critical metabolites by LC-MS/MS. The image below was obtained from the study results.
Galani et al., 2018 Conducted a study on the residues of 99 pesticides in 72 samples of 12 agricultural products collected in the region, using QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, and Safe) method extraction, and analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). From the results, it was evident that Twenty-one pesticides (34.4%) exceeded their European Union maximum residue limits (MRLs), and 22 pesticides (34.4%) were found in all six sampling locations. Malathion and p,p′-DDT were the most distributed pesticides found in almost all the samples and sampling sites. The Figure below illustrates the results that were obtained and the food items that were tested Figure 5, Figure 6.
Figure 5.Aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, deoxynivalenol, zearalenone in breast milk https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04576#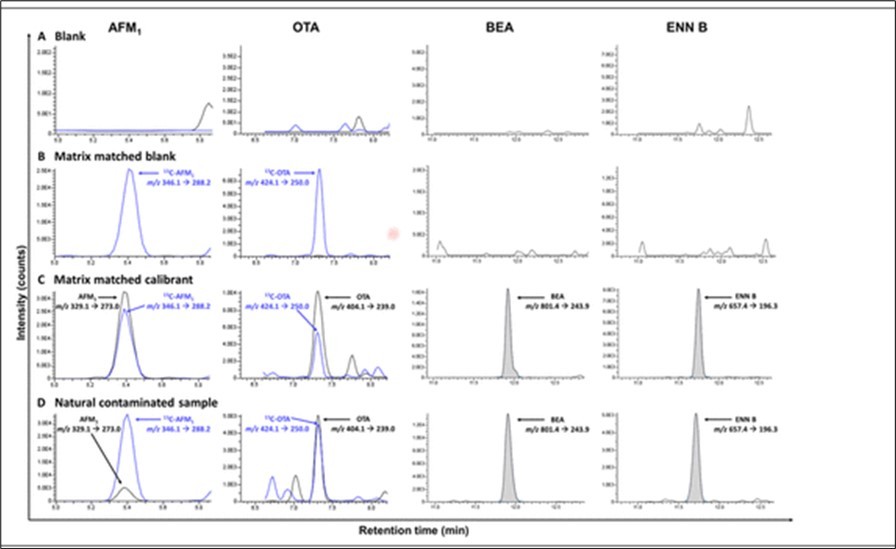
Figure 6.The results of the food items and pesticides that were found on them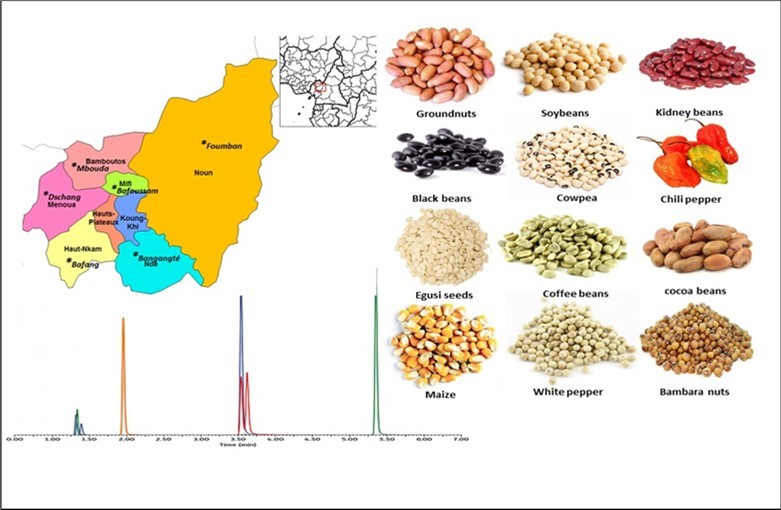
Conclusion
Chemistry, as a scientific learning area, has been able to come up with various techniques and applications that can be applied in a variety of places in society, such as the aspect of food security. The term food security should be illustrated as the providence of the necessary analysis and suitable practices and methods that will result in a healthier and more adaptable society. As described in the study above, various chemical processes can be applied to determine the food safety perspectives that currently exist in society. Such will allow the attainment of sustainable development goals, among other international goals that are geared towards making sure that the society is well-fed with quality food. In the process of food production, there are situations in which the food in the society can be terminated as a result of harmful farming practices, lack of suitable storage facilities or even when there are conditions in which food items cannot be stored for long periods. As a result of such action, there is a need for an analysis of the various food items to determine whether they are applicable for human consumption. Lack of such measures can result in the development of illness, among other conditions that are likely to affect human society to a greater extent.
There are various ways in which food can be analyzed in the field of chemistry, and each of the methods may be able to be analyzed either quantitatively or qualitatively. One such method is the utilization of liquid chromatography (LC-MS). As a result, the passage of the specimen, both in the liquid chromatography and the mass spectrometry area, resulted in the analysis of the samples and intended. The primary role of liquid chromatography is to assist in the separation of the various components that are found in the liquid phase. On the other hand, the MS allowed the illustration of the quantity of a specific specimen contained in a sample. Thus, the LCMS method is applicable to the determination of food safety as it has the capacity to analyze different species and species that are currently under investigation. In the illustration above, various studies have been utilized to demonstrate the utilization of the LC-MS technique in the management of food safety operations in society.
Even though there are various drawbacks to the utilization of the LC-MS in the food safety aspect, the primary being the cost and the operation management of the technique, it should be noted that healthy food results in a healthy society. As such, the various government entities that have been tasked with the analysis of the food items that are being eaten by society should be able to ensure that the quality of the food that is being eaten in society is up to standard. Also, industries should be able to acquire such instruments in the providence of the quality services to the society
The study, therefore, recommends the utilization of various scientific techniques in the promotion and management of food safety and security in society. We are what we eat is a saying that is commonly used when referring to the quality of food that one consumes. As such, it is expected that production and preparation should be able to ensure that the different food items that are consumed in society abide by the set regulated standards.
References
- 1.Fung F, H S Wang, Menon S. (2018) . Food safety in the 21st century. Biomedical journal 41(2), 88-95.
- 2.King T, Cole M, J M Farber, Eisenbrand G, Zabaras D et al. (2017) Food safety for food security: Relationship between global megatrends and developments in food safety. , Trends in Food Science & Technology 68, 160-175.
- 3.F P Carvalho. (2017) Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food and energy security. 6(2), 48-60.
- 4.L M Zanin, Cunha da, T D, Rosso V V de, V D Capriles et al. (2017) Knowledge, attitudes and practices of food handlers in food safety: An integrative review. Food research international. 100, 53-62.
- 5.World Health Organization. (2021) Antimicrobial resistance and the United Nations sustainable development cooperation framework: Guidance for United Nations Country teams. World Health Organization.
- 6.Badri A, Boudreau-Trudel B, A S Souissi. (2018) Occupational health and safety in the industry 4.0 era: A cause for major concern?. , Safety science 109, 403-411.
- 7.Gallo M, Ferrara L, Calogero A, Montesano D, Naviglio D. (2020) Relationships between food and diseases: What to know to ensure food safety. , Food Research International 137, 109414.
- 8.Asselt E D Van, Arrizabalaga-Larrañaga A, Focker M, Berendsen B J A, Schans M G M Van de et al. (2023) Chemical food safety hazards in circular food systems: A review. Critical Reviews. in Food Science and Nutrition 63(30), 10319-10331.
- 9.Li C, Li C, Yu H, Cheng Y, Xie Y et al. (2021) Chemical food contaminants during food processing: sources and control. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. 61(9), 1545-1555.
- 10.Pakdel M, Olsen A, Bar E M S. (2023) A review of food contaminants and their pathways within food processing facilities using open food processing equipment. , Journal of Food Protection 86(12), 100184.
- 11.Arena K, Mandolfino F, Cacciola F, Dugo P, Mondello L. (2021) Multidimensional liquid chromatography approaches for analysis of food contaminants. , Journal of separation science 44(1), 17-34.
- 13.C R Baiz, Błasiak B, Bredenbeck J, Cho M, J H Choi et al. (2020) Vibrational spectroscopic map, vibrational spectroscopy, and intermolecular interaction. , Chemical reviews 120(15), 7152-7218.
- 14.Debus B, Parastar H, Harrington P, Kirsanov D. (2021) Deep learning in analytical chemistry. , TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 145, 116459.
- 15.Chen C, Hou J, J, Cheng J. (2020) Bioinformatics methods for mass spectrometry-based proteomics data analysis. International journal of molecular sciences. 21(8), 2873.
- 16.Shi L, M P Bucknall, T L Young, Zhang M, Hu L et al. (2020) Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analyses of encapsulated stable perovskite solar cells. , Science 368(6497), 2412.
- 17.Tamara S, Boer M A den, A J Heck. (2021) High-resolution native mass spectrometry. , Chemical Reviews 122(8), 7269-7326.
- 18.Kulyyassov A, Fresnais M, Longuespée R. (2021) Targeted liquid chromatography‐tandem mass spectrometry analysis of proteins: Basic principles, applications, and perspectives. , Proteomics 21(23), 2100153.
- 19.A B Kanu. (2021) Recent developments in sample preparation techniques combined with high-performance liquid chromatography: A critical review. , Journal of Chromatography A 1654, 462444.
- 20.Siddique I. (2021) Unveiling the Power of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: Techniques, Applications, and Innovations. , European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology 8(9), 79-84.
- 21.S N Thomas, French D, P J Jannetto, B A Rappold, W A Clarke. (2022) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for clinical diagnostics. Nature Reviews Methods Primers. 2(1), 96.
- 22.T I Ekwomadu, T A Dada, S A Akinola, Nleya N, Mwanza M. (2021) Analysis of selected mycotoxins in maize from north-west South Africa using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and other analytical techniques. , Separations 8(9), 143.
- 23.López-Fernández O, Domínguez R, Pateiro M, P E Munekata, Rocchetti G et al. (2020) Determination of polyphenols using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry technique (LC–MS/MS): A review. , Antioxidants 9(6), 479-32498428.
- 24.Arce-López B, Lizarraga E, Flores-Flores M, Irigoyen Á, González-Peñas E. (2020) Development and validation of a methodology based on Captiva EMR-lipid cleanup and LC-MS/MS analysis for the simultaneous determination of mycotoxins in human plasma. , Talanta 206, 120193.
- 25.J Y Bae, D Y Yun, N S Kang, W J Choe, Y H Jeong et al. (2023) Investigation on pesticide residues in agricultural products in domestic markets using LC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS. , Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety 38(3), 131-139.
- 26.Bessaire T, Mujahid C, Mottier P, Desmarchelier A. (2019) Multiple mycotoxins determination in food by LC-MS/MS: An international collaborative study. , Toxins 11(11), 658.
- 27.Braun D, C N Ezekiel, W A Abia, Wisgrill L, G H Degen et al. (2018) Monitoring early life mycotoxin exposures via LC-MS/MS breast milk analysis. , Analytical chemistry 90(24), 14569-14577.
- 28.B De Santis, Debegnach F, Gregori E, Russo S, Marchegiani F et al. (2017) Development of a LC-MS/MS method for the multi-mycotoxin determination in composite cereal-based samples. , Toxins 9(5), 169.